ACL Tears
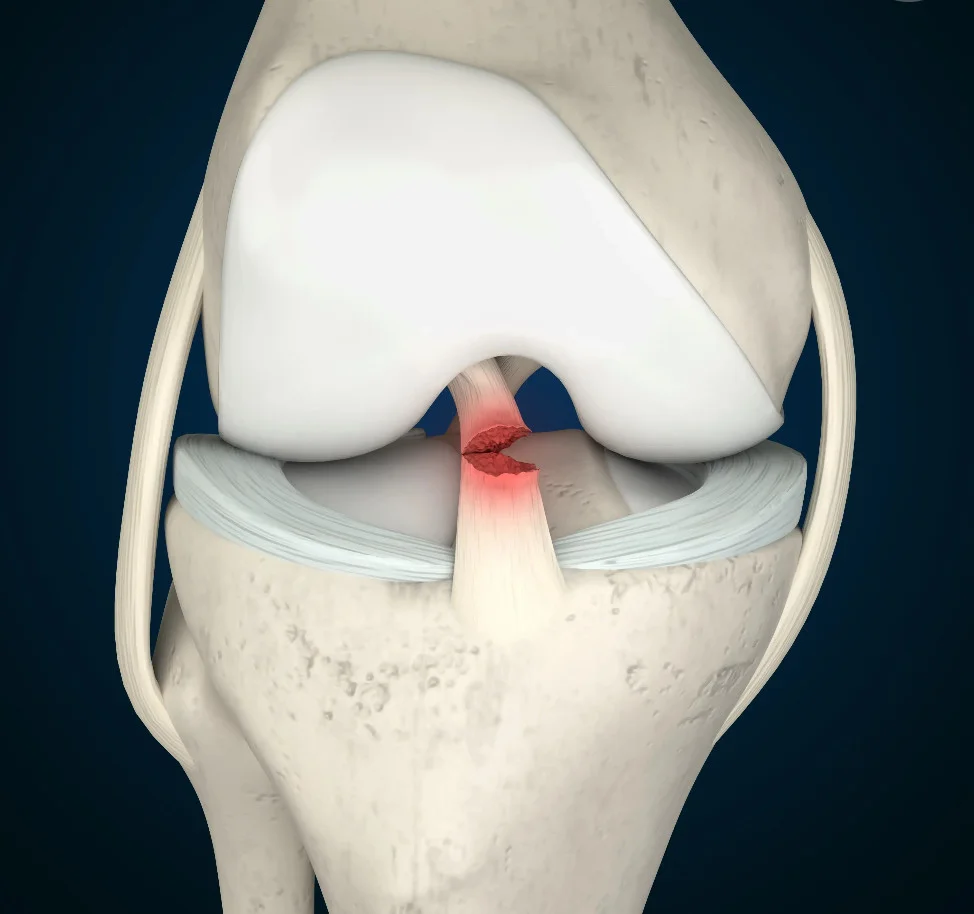
A common knee ligament injury that can affect stability, function, and performance
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that helps stabilise your knee joint. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and plays an important role in controlling forward movement and rotation of the knee. An ACL tear is a common injury, especially among athletes and physically active individuals. It can occur during sudden stops, pivots, changes in direction, or direct impacts to the knee.
Dr George Awwad provides thorough assessment, diagnostic imaging, and tailored treatment for ACL tears, from conservative management to surgical reconstruction, depending on your activity level, lifestyle, and injury severity.
Signs and symptoms of an ACL tear
An ACL tear is typically associated with a noticeable injury event and may include the following symptoms:
While a complete ACL rupture often causes obvious symptoms, partial tears or associated injuries to other structures (e.g., meniscus, MCL) may also contribute to discomfort and loss of function.
- A loud pop or “popping” sensation at the time of injury
- Sudden onset of knee pain and swelling, usually within the first few hours
- Instability or a feeling of the knee “giving way”, especially during turning or pivoting motions
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness
- Ongoing symptoms of instability or weakness during sport or daily activities
Causes and risk factors
ACL tears are most often associated with sporting activities that involve:
- Sudden stops or changes in direction (e.g., soccer, netball, basketball)
- Pivoting or twisting motions while the foot is planted
- Landing awkwardly from a jump
- Direct contact or trauma to the knee (e.g., during tackles)
Women are statistically more likely to sustain ACL injuries due to a combination of anatomical, hormonal, and biomechanical factors.
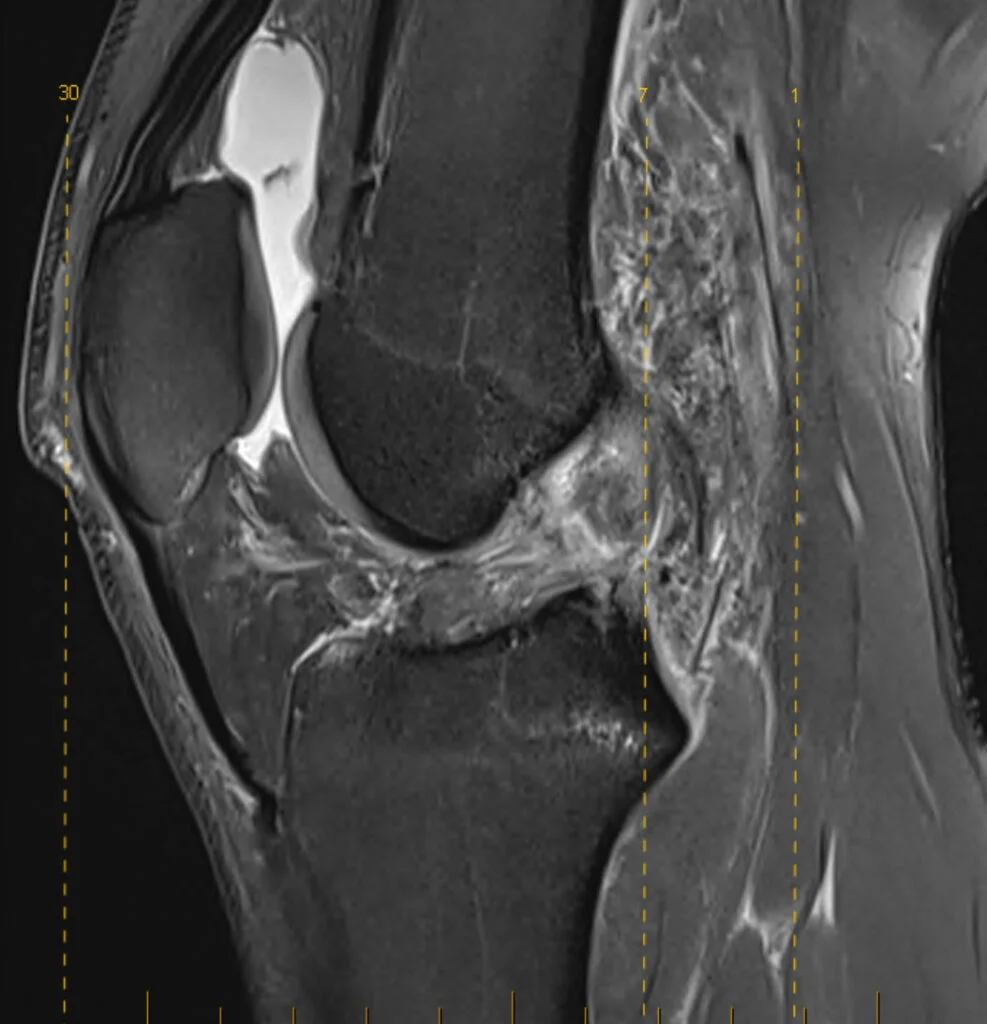
Diagnosing an ACL tear
Dr Awwad will begin with a detailed history and physical examination to assess your knee stability, swelling, and range of motion. Specific clinical tests such as the Lachman test and pivot shift test help assess the integrity of the ACL.
Imaging may include:
- X-rays: Used to rule out fractures or associated bony injuries
- MRI scan: The most accurate way to confirm a complete or partial tear and assess other internal knee injuries such as meniscal tears or bone bruising
A prompt and accurate diagnosis helps determine whether non-surgical or surgical treatment is most appropriate.
Treatment options for ACL injuries
Non-surgical treatments
- Physiotherapy to improve strength, stability, and range of motion
- Bracing to support the knee during activity
- Activity modification to avoid instability and further injury.
- Hamstring tendon
- Quadriceps tendon
- Patellar tendon
- Allograft (donor tissue, used in select cases)
Book a consultation

If you’ve experienced a knee injury or are living with symptoms of instability, Dr George Awwad can provide a comprehensive assessment and discuss whether ACL reconstruction is suitable for you. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment may help you return to your chosen activities with improved stability and confidence.
